Elderberry has been recognized for its medicinal properties for centuries, particularly in regions like Greece, Scandinavia, Portugal, and Morocco. It’s a globally common medicinal plant used in traditional medicine for various ailments such as fever, rheumatism, sciatica, infections, and more. The most prevalent type, Sambucus nigra or European elderberry, is known for its clusters of white and cream flowers and bunches of berries.
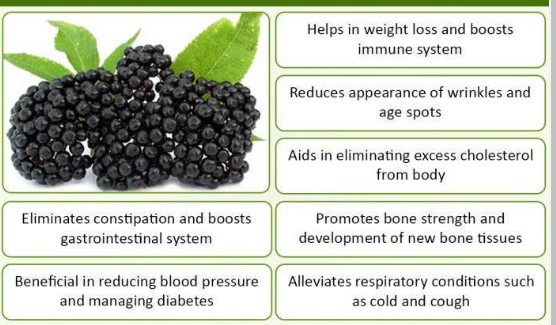
Notable for its rich antioxidant content and anti-inflammatory properties, elderberry is primarily used today for treating cold and flu symptoms.
Each cup of elderberry offers a substantial amount of vitamin C (52.2 mg), aiding immune health, illness prevention, and muscle recovery.
Moreover, the high antioxidant levels in elderberry, including compounds like protocatechuic and chlorogenic acid, contribute to its health benefits. These antioxidants protect cells from oxidative damage, which can lead to various diseases.
Elderberry also promotes heart health by lowering inflammation, cholesterol, and blood pressure. Its role in reducing inflammation extends to improving mental health and mood. Additionally, elderberries can boost immune system functioning, helping to recover from respiratory illnesses more quickly. Although not a preventive measure for illnesses, elderberry can shorten the duration of sickness.
For respiratory and lung health, elderberries contain quercetin, a flavonoid known to support lung function, particularly beneficial for conditions like asthma and COPD. Its high fiber content contributes to a healthy gut, digestion, and immune system, while also aiding in blood sugar management.
Elderberry can also be useful for easing sore throats and coughs, especially when used in specific forms like lozenges or extracts. Its antioxidants are beneficial for maintaining healthy skin, protecting against cellular damage, and promoting a youthful appearance.
When consuming elderberry, it’s essential to cook the berries to avoid risks like cyanide poisoning, which can occur from eating them raw. Avoiding the plant’s bark, leaves, and seeds is also advised due to their potential laxative and diuretic effects.
Elderberry can be incorporated into the diet through various forms, including syrups, jams, jellies, and supplements like gummies. It’s particularly recommended during winter or flu season, and starting consumption at the onset of cold or respiratory symptoms can be effective.
Regarding dosage and safety, elderberry should be consumed in moderation, with typical dosages ranging from 5-15 milliliters. However, it’s crucial to consult a healthcare provider before starting any supplements, especially for pregnant women or individuals with specific allergies.
In summary, elderberries offer multiple health benefits, particularly in supporting immune health and treating respiratory conditions. While beneficial, it’s essential to use elderberry supplements cautiously and under professional guidance to ensure safety and effectiveness.
References:
